研究背景
传统的肿瘤药物递送因复杂的微环境面临渗透困难、效率低的瓶颈,而肿瘤细胞自身却存在通过隧道纳米管等结构进行线粒体交换的天然运输网络。本研究受到这一现象的启发,通过调控线粒体自噬增强线粒体的细胞间转运能力,并利用其作为“生物载体”搭载治疗药物,构建了一种能够突破肿瘤屏障、实现深层递送的新型线粒体自主驱动系统,为肿瘤精准治疗提供了新策略。
助力研究
2025年12月23日,北京大学药学院齐宪荣教授团队在《Nature Communications》发表了题为“Leveraging engineered mitochondria through intercellular communication network for accelerated transport and delivery”的研究论文。通过调控线粒体自噬、利用细胞间隧道纳米管网络,构建了“线粒体自主驱动系统”,实现了光敏药物的高效、深层、可控递送,为肿瘤精准治疗提供了创新策略。
在该研究中,艾锐Polar-SIM结构光超分辨显微系统发挥了至关重要的作用,尤其是在揭示线粒体在细胞间高速、双向运输的动态行为方面,提供了直观成像数据。

Polar-SIM在该文中的贡献
观察抑制线粒体自噬下在TNTs中线粒体的运动性和双向运输。
线粒体如何通过细胞间隧道纳米管进行运输,其速度和模式是关键机制问题。该研究利用Polar-SIM的超高时空分辨率,对标记了线粒体和TNTs(F-actin)的活细胞进行长达20分钟的长时程动态成像,清晰捕捉到单个线粒体在TNT中从供体细胞穿梭至受体细胞的全过程。轨迹分析显示,线粒体在TNT中的运动速度显著提升(是对照组的2.0倍),位移距离也更长,首次以直观、定量的方式证明了通过抑制线粒体自噬可以增强其细胞间转运能力。
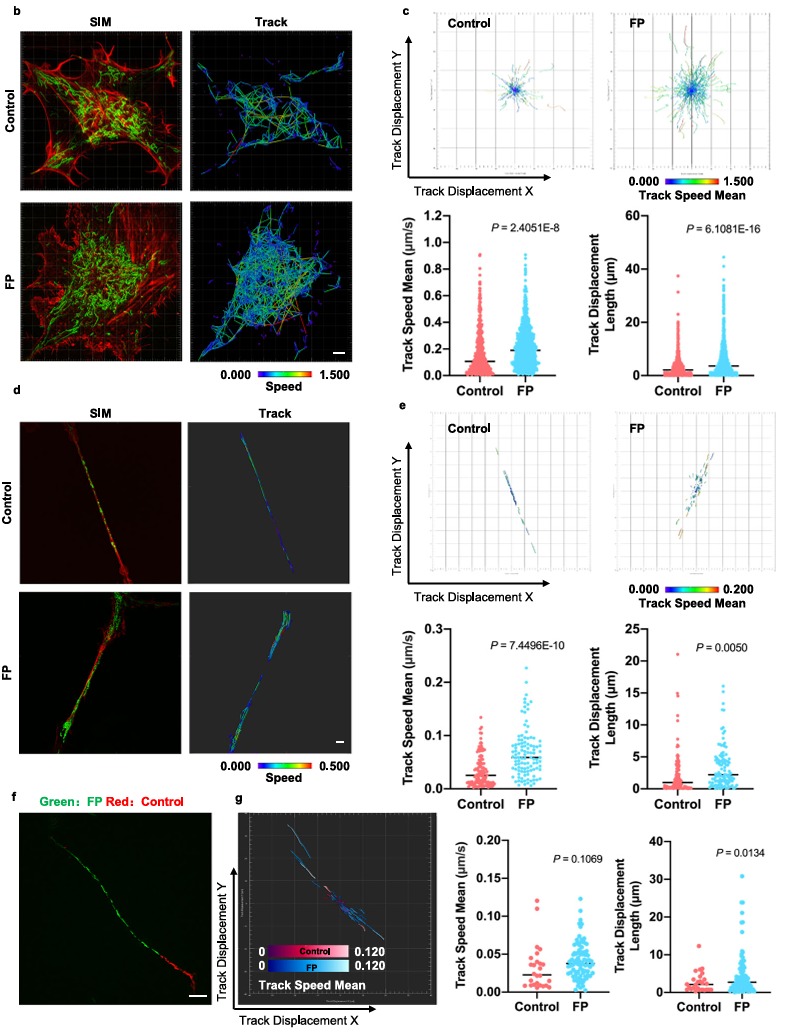
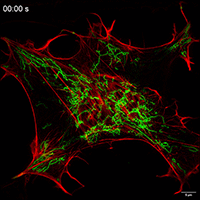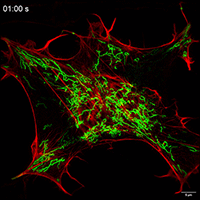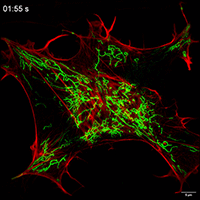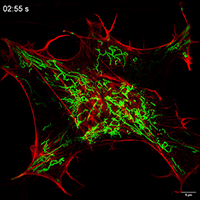
Figure 3. Inhibition of mitophagy increases mitochondrial motility and bidirectional transport. (b) SIM images and speed-position tracks of mitochondrial movements and (c) mean track speed-displacement maps in individual cells over a three-minute period. Red: cytoskeleton (F-actin). Green: mitochondria. Scale bar: 5 µm. (n=498 mitochondria for control, n=885 mitochondria for FP). (d) SIM images and speed-position tracks of mitochondrial movements and (e) mean track speed-displacement maps in TNTs between cells over a twenty-minute period. Red: TNTs (F-actin). Green: mitochondria. Scale bar: 5 µm. (n=120 mitochondria for control, n=106 mitochondria for FP). (f) SIM images of mitochondrial movements and (g) mean track speed-displacement maps between untreated and PINK1 knockout cells over a ten-minute period. Red: mitochondria in untreated cells (Control). Green: mitochondria in PINK1 knockout cells (FP). Scale bar: 10 µm. (n=26 mitochondria for control and n=84 mitochondria for FP). For Figure (c, e, g), the starting position of mitochondrial trajectory was uniformly set as the origin in the coordinate system. Mean track speed and displacement length of all mitochondrial trajectory was counted and analyzed. Data were presented as mean ± SD. P values were determined using two-tailed unpaired t test (a, c, e, g).
图3.抑制有丝分裂可增加线粒体的运动性和双向运输。(B)线粒体运动的SIM图像和速度-位置轨迹,以及(C)单个细胞在三分钟内的平均轨迹速度-位移图。红色:细胞骨架(F-肌动蛋白)。绿色:线粒体。标尺:5 μm。(对照为498个线粒体,FP为885个线粒体)。(D)线粒体运动的SIM图像和速度-位置轨迹,以及(E)细胞间TNTs在20分钟内的平均轨迹速度-位移图。红色:TNTs(F-肌动蛋白)。绿色:线粒体。比例尺:5 μm。(对照为120个线粒体,FP为106个线粒体)。(F)线粒体运动的SIM图像和(G)10分钟内未处理细胞和PINK1基因敲除细胞之间的平均速度-位移图。红色:未处理细胞中的线粒体(对照)。绿色:PINK1基因敲除细胞(FP)的线粒体。标尺:10 μm。(对照组26个线粒体,FP组84个线粒体)。对于图(c,e,g),将线粒体轨迹的起始位置统一设置为坐标系中的原点。统计和分析所有线粒体轨迹的平均轨迹速度和位移长度。数据以平均±标准差表示。P值采用双尾非配对t检验(a,c,e,g)。
Movie 1 Mitochondrial movements within cell of Control group.
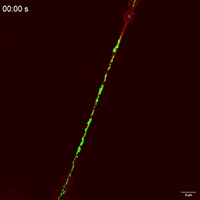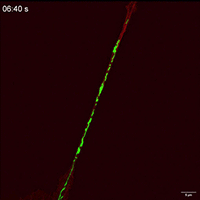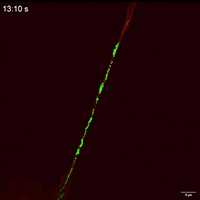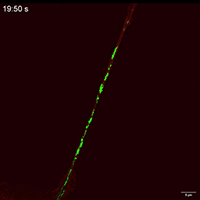
Movie 2 Mitochondrial movements within cell of FP group.
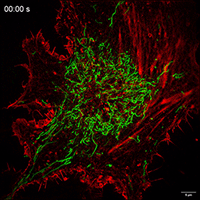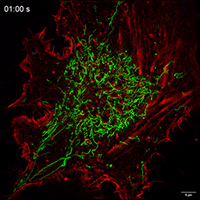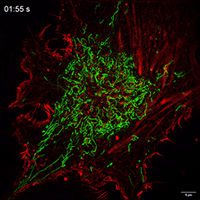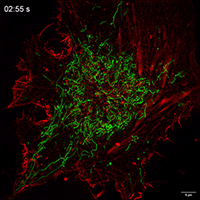
Movie 3 Mitochondrial movements within TNT of Control group.
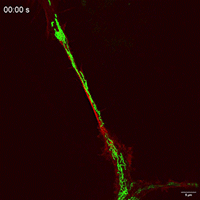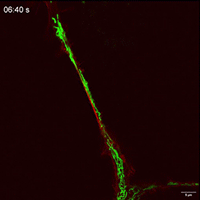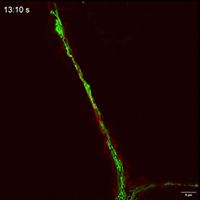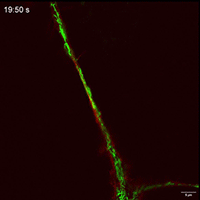
Movie 4 Mitochondrial movements within TNT of FP group.
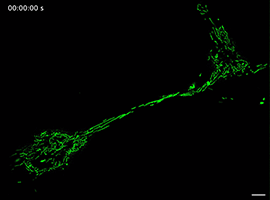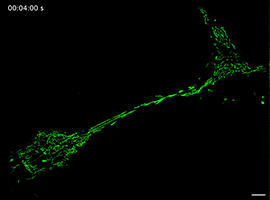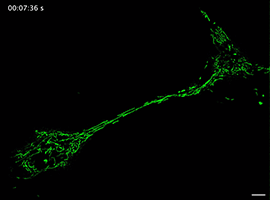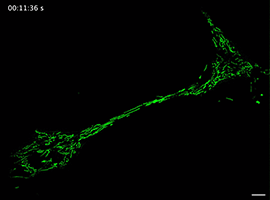
Movie 5 Long-term imaging of a mitochondrion transporting from one cell to another in FP group.
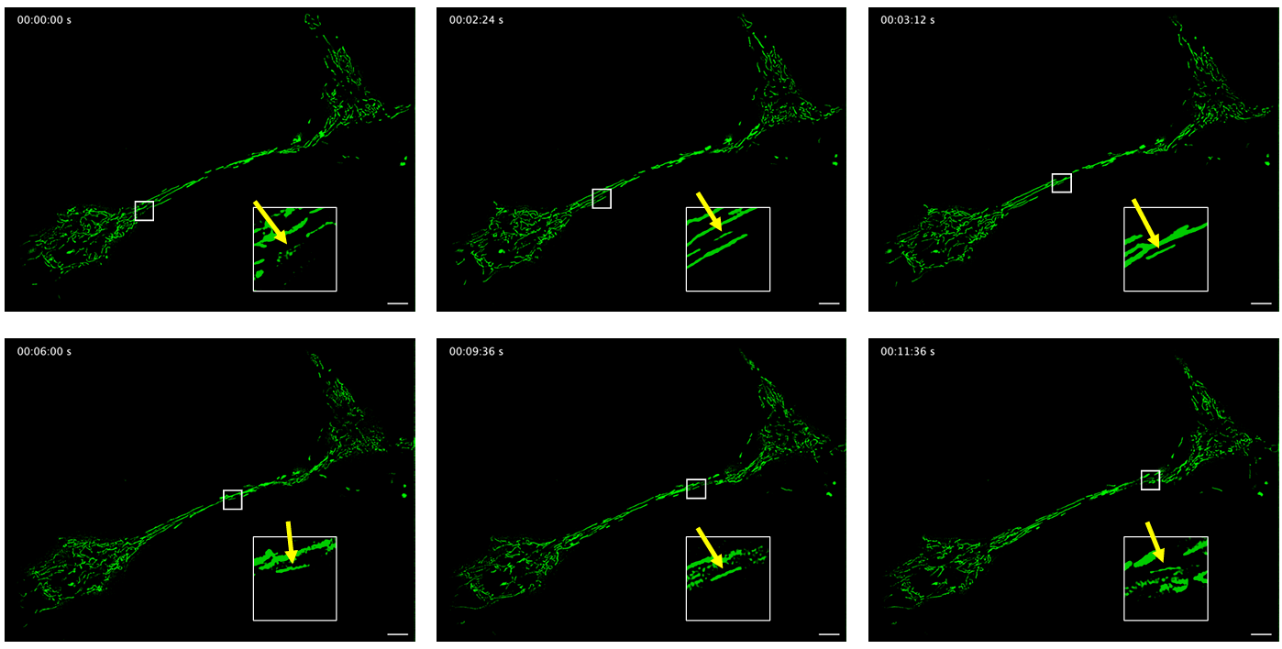
Supplementary Figure S9. Intercellular mitochondrial transfer. Images of mitochondria transferring from one cell to another. Yellow arrows indicate the Negative Control FP Positive Control transferring mitochondria. Green: mitochondria. Scale bar: 5 µm.
补充图 S9. 细胞间线粒体转移。线粒体从一个细胞转移到另一个细胞的图像。黄色箭头指示转移中的线粒体。绿色:线粒体。比例尺:5 μm。
总结
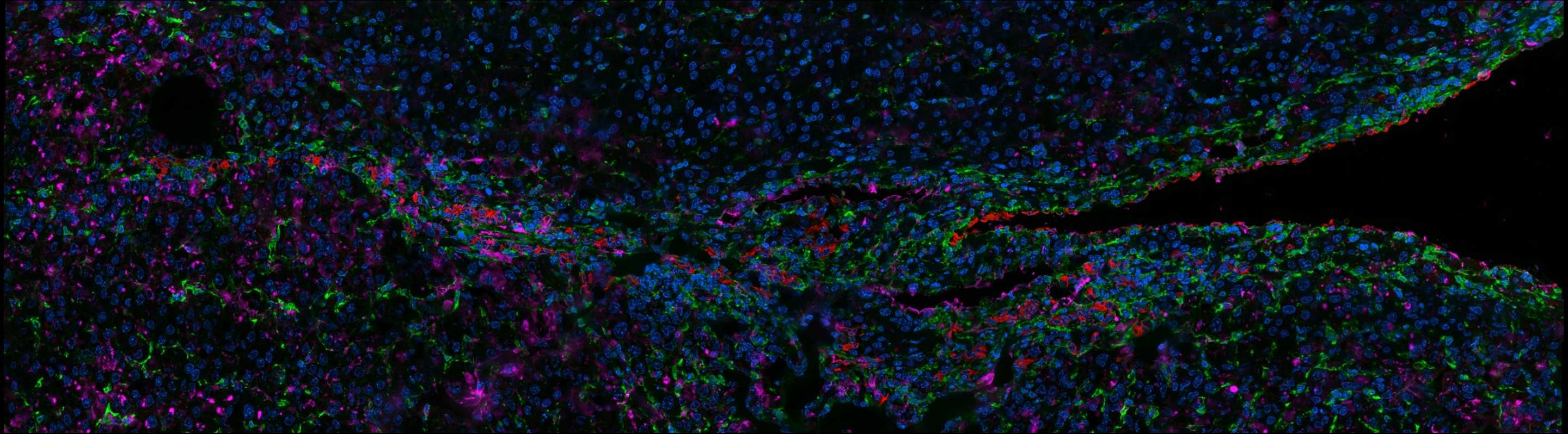
本研究创新性地提出利用线粒体作为药物载体,通过TNTs实现细胞间的药物传递,从而实现高效的细胞间药物递送。这种策略不仅提高了药物的传递效率,还避免了传统纳米载体可能带来的免疫反应和清除问题。首次在活体肿瘤组织切片中直接观察到连接两个细胞的TNTs结构,并与IR780荧光存在强烈重叠,为细胞间通讯机制提供证据。首次系统揭示了通过调控线粒体自噬可以主动增强线粒体胞间传输能力。构建高速交通网络,生产药物可搭乘的“线粒体车辆”,并为其赋能。
艾锐Polar-SIM超分辨成像系统在本研究中发挥了关键作用。其具备高分辨率、低光毒性的特点,能够在活细胞条件下清晰解析线粒体、TNT等亚细胞结构的动态行为,并支持长时程成像,直接捕捉到线粒体搭载药物沿TNT穿梭的过程,为机制验证与定量分析提供了不可或缺的可视化证据。
彭祎玮和高达同为第一作者。齐宪荣为通讯作者。研究得到国家自然科学基金的资助。
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-67837-8




 公安备案号:京公网安备11010802046288号
公安备案号:京公网安备11010802046288号